In recent years, the term blockchain technology has become a buzzword in the fields of finance, technology, and even everyday life. But what exactly is blockchain technology? This article aims to demystify blockchain, exploring its definition, underlying principles, applications, and future potential. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or a beginner looking to understand the basics, this guide will provide you with all the essential information.
H1: Understanding Blockchain Technology
H2: Definition of Blockchain Technology
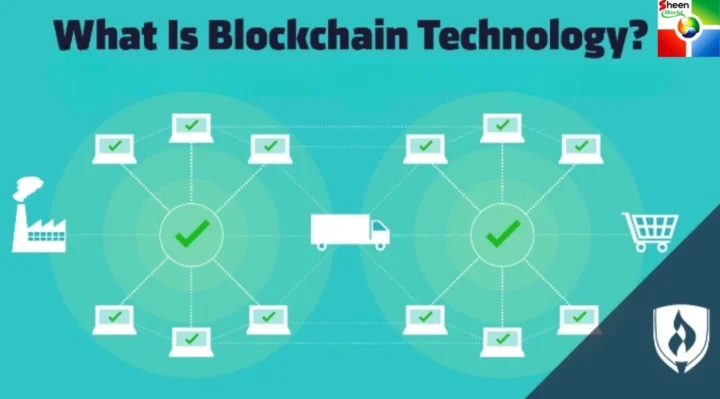
At its core, blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in such a way that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively. This technology ensures transparency, security, and immutability, making it a revolutionary advancement in data management.
H3: How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain operates through a series of interconnected blocks that contain transaction data. Each block has three primary components:
- Data: This includes the transaction details, such as the amount transferred, the sender, and the receiver.
- Hash: Each block contains a unique hash that serves as a digital fingerprint, linking it to the previous block.
- Previous Block Hash: This ensures that each block is tied to the block before it, creating a chain.
When a new transaction occurs, it is verified by network participants, added to a new block, and then linked to the existing blockchain. This decentralized mechanism prevents data manipulation and enhances security.
H4: The History of Blockchain Technology
The concept of blockchain technology was first introduced in 2008 by an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It was implemented as the underlying technology behind Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, launched in 2009. Since then, blockchain has evolved beyond cryptocurrencies, finding applications in various sectors.
H1: Key Features of Blockchain Technology
H2: Decentralization
One of the most significant features of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional databases controlled by a central authority, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network. This decentralization enhances security and reduces the risk of a single point of failure.
H3: Transparency
Blockchain technology promotes transparency through public access to transaction records. Every participant in the network can view the entire history of transactions, fostering trust and accountability among users.
H4: Immutability
Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability is achieved through cryptographic hashing, making blockchain an ideal solution for industries where data integrity is crucial, such as finance and healthcare.
H1: Types of Blockchain Technology
H2: Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open to anyone and allow anyone to participate in the network. Bitcoin and Ethereum are prime examples of public blockchains. They are transparent and decentralized, making them suitable for cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications (dApps).
H3: Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are restricted to a specific group of users. Organizations often use them for internal processes, providing greater control over data and transactions. Hyperledger and Corda are examples of private blockchains.
H4: Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are governed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. They strike a balance between decentralization and control, making them suitable for industries like finance, where multiple institutions collaborate.
H1: Applications of Blockchain Technology
H2: Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of blockchain technology is cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others operate on blockchain networks, allowing for peer-to-peer financial transactions without the need for intermediaries.
H3: Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains. By recording every step of a product’s journey on the blockchain, companies can ensure authenticity and reduce fraud.
H4: Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain can securely store patient records, enabling interoperability between different healthcare providers while maintaining patient privacy. This can lead to better patient care and streamlined processes.
H1: Challenges of Blockchain Technology
H2: Scalability
One of the primary challenges facing blockchain technology is scalability. As the number of users and transactions increases, the network can become congested, leading to slower transaction times and higher fees.
H3: Energy Consumption
Many blockchain networks, particularly those that use proof-of-work consensus mechanisms (like Bitcoin), consume significant amounts of energy. This has raised concerns about the environmental impact of cryptocurrencies.
H4: Regulation
The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Governments are grappling with how to regulate these technologies without stifling innovation.
H1: The Future of Blockchain Technology
H2: Potential Developments
The future of blockchain technology is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at addressing current challenges. Innovations like proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms and layer 2 solutions aim to improve scalability and energy efficiency.
H3: Integration with Other Technologies
Blockchain technology is expected to integrate with other emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics. This integration can create new use cases and enhance existing applications.
H4: Increased Adoption Across Industries
As awareness of blockchain technology grows, more industries are likely to adopt it for various applications, from finance and healthcare to real estate and voting systems. This increased adoption can lead to a more decentralized and transparent future.
H1: Conclusion
In summary, blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to data management, emphasizing decentralization, transparency, and security. While it faces challenges such as scalability and regulatory concerns, the potential applications and future developments make it a technology worth following. As industries continue to explore its capabilities, blockchain may reshape the way we conduct business and interact in the digital world.
By understanding what blockchain technology is, its features, applications, and future prospects, individuals and organizations can better prepare for the changes it will bring. Whether you are a business leader, tech enthusiast, or simply curious about the digital landscape, grasping the fundamentals of blockchain will be essential in navigating the future.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at what blockchain technology is, covering its definition, key features, applications, and future potential. Whether you’re new to the concept or looking for a more thorough understanding, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to engage with this transformative technology.



